USA

About USA
The USA currency is crowned as the world’s reserve because it is one of the most superpower economies.
Location
The USA (United States of America) is located in North America. It is bordered by Canada to the north, Mexico to the south,The Atlantic Ocean to the east,The Pacific Ocean to the west

Why is the USA an ideal study abroad destination ?

- USA is a Hub of world renowned universities.
- Few universities in the USA give admission on the basis of MOI.
- Tuition fees charged by the USA universities are quite affordable.
- In case of IELTS, only overall bands are considered. For UG program O/B should be minimum 6 whereas for PG the requirement is 6.5.
- Students receive their I-20s & offer letters just within a month. However, few universities do not ask for an I-20 deposit.
- Fully furnished accommodation facilities are provided by each university.
- And lastly, USA universities are popular for offering the highest amount of scholarships.
Top 10 universities

Stanford University

Northwestern University

Duke University

Johns Hopkins University

Boston University

Purdue University

University of southern California

Cleveland State University

Washington University

Arizona State University
USA Tuition fees
Courses | Minimum annual | Maximum annual |
| Bachelor | $ 32,000 | $ 45,000 |
| Master | $ 22,000 | $ 30,000 |
| Diploma | $ 6000 | $ 20,000 |
| Ph.D | $ 10,000 | $ 50,000 |
| Intakes | September, January, May | |
Supportive Student Services
-
International Student Office (ISO): Located within most universities; provides visa guidance, academic support, social integration programs, and general advice for international students.
-
NAFSA: Association of International Educators: A professional organization that supports international education and exchange. Offers resources, conferences, and guidance on immigration, cultural adaptation, and professional development.
-
Education USA: U.S. Department of State network of advising centers worldwide. Provides information on U.S. higher education, scholarships, visa guidance, and pre-departure orientations for international students.

-
Institute of International Education (IIE): Offers scholarships, fellowships, and grants for international students. Manages programs like Fulbright and other international exchange programs.
-
International Student.com: An online resource offering information on studying in the U.S., including visas, scholarships, health insurance, and financial advice. Provides a platform for community support and student blogs.

-
International Students Organization (ISO): Student-run organizations at many U.S. universities offering social, cultural, and networking events to help international students integrate into campus life.
-
The Fulbright Program: Provides scholarships and grants for international students pursuing higher education and research in the USA. Supports cross-cultural exchange and academic excellence.
-
United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS): Provides official guidance on visa regulations, Optional Practical Training (OPT), Curricular Practical Training (CPT), and other immigration-related matters for international students.
-
Open Doors (IIE): Provides data and statistics on international students studying in the USA. Helps universities and policymakers create better support systems for international students.
-
Council on International Educational Exchange (CIEE): Offers study abroad programs, intercultural exchange, and scholarships for international students. Provides guidance on adapting to American culture and education systems.
Cost of living
Accommodation
$ 800 to $ 2500
Food
$ 100 to $ 500
Educational Materials
$ 50 to $ 100
Transportation
$ 50 to $ 970
Personal Expenses
$ 100 to $ 300
Utilities
$ 100 to $ 200
Health Insurance
$ 100 to $ 300
Estimated Total Cost
$ 1,400 to $ 5,500
Weather
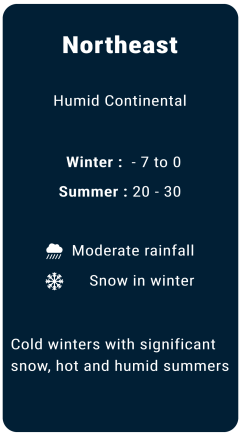
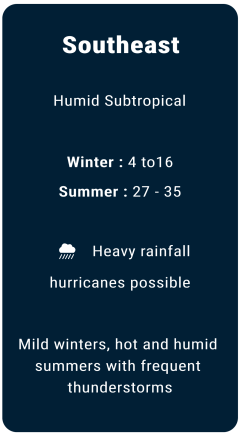
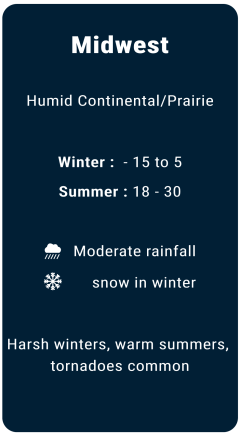
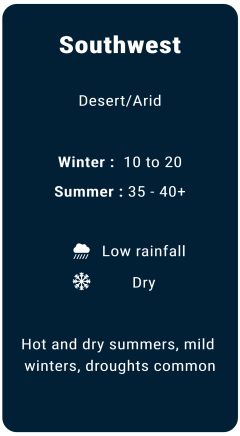
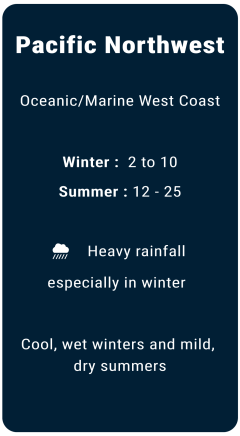
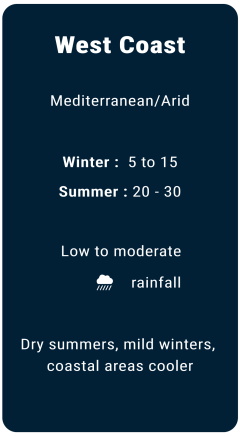
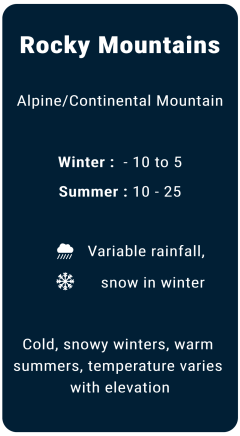



Major local banks in USA
Chase Bank
Bank of America
Wells Fargo
PNC Bank
Citibank
HSBC Bank USA
Capital One
TD Bank
Mobile Network Operator











United States of America (USA) - States
Top Universities
FAQ
You do not declare a major until the end of you second year of school.
It depends: Some degree programs are highly structured. Bachelors’ degrees are very flexible and sometimes allow you to create your own program.
Each U.S. university will want to review an international student’s subjects and may ask the student to contact a credential evaluation agency.
U.S. institutions cannot issue I-20 forms for non-degree study, including vocational training. Community colleges offer technical/vocational study for an associate’s degree.
Attend the closest Education USA advising center’s predeparture orientation. Then, when you arrive on campus, attend all orientation meetings scheduled at your college or university.
Distance education occurs when a student and an instructor are in different places. Learning occurs by mail, telephone, internet, or by other means.
U.S. universities require an English language proficiency test before admission to ensure you can read, write, and speak fluently.
Grade Point Average (GPA) is a numeric indicator for a student’s academic performance, calculated on a scale of 4.0.
A credit is a value assigned to each course which reflects the number of hours the class will meet with the professor each week.
Essentially there is no difference.
There are a number of programs for English language study in the United States and online, as well as local possibilities.
MBA programs typically last one to two years.
With permission of the International Student Office, international students may work on campus up to 20 hours/week their first year and can apply to work off-campus in subsequent years.
Associate: a two-year program that either leads to a specific vocation or transitions to a bachelor program. Bachelor: a four or five-year program where students earn credits in a wide variety of courses.
In a joint-degree program, students begin a graduate program in their fourth year of college, earning both degrees upon graduation.
Yes, but they are highly selective and require a heavy courseload across a total of six years of study.
The academic year usually runs from August through May with breaks for holidays. Most universities use either the semester system (two terms), the quarter system (students attend three out of four total terms), or the trimester system (three terms).
Yes, although you may lose some credits and require extra time to complete your degree.
Colleges offer only undergraduate degrees while universities offer graduate degrees as well, but the terms are often used interchangeably.
In general, you must have completed high school and you must be at least 17 years of age.
Undergraduate programs follow high school and lead to an associate (two-year) degree or a bachelor (four-year) degree. Graduate programs follow a bachelor’s degree and lead to a master’s or doctoral degree.
Yes. To find accredited online distance learning programs, please search the Distance Education Accrediting Commission website.
Community colleges are typically state-supported and provide the first two years of a four-year undergraduate degree.
You must fulfill the requirements of a freshman applicant, as well as any supplemental information required by the transfer institution.
Community colleges offer lower costs, easier admission policies, close ties to state schools,and many of the required courses connected to a degree.
The transfer process varies for each school. It is best to target the four-year institution early and determine what is needed to transfer.
Refer to college and university guides to find which institutions are known for excellence in different fields of study.
State universities are funded by the state and are generally larger and less expensive than private universities.
Grades are typically determined by quizzes, midterms, final exams, papers, projects, class attendance, and class participation.
Contact the office responsible for international programs at your institution to ask if your school has exchange agreements with U.S. universities.
Letter grades indicate a student’s academic performance. Each letter grade has a numeric value which is used to calculate a GPA, on a scale of 4.0.
Search the U.S. Department of Education’s Office of Post-secondary Education website to see if an institution is accredited.
For specialized program accreditation, see “Accredited Institutions of Postsecondary Education,” available from American Council on Education.



















